: 파일/표준입력의 첫부분 10라인을 출력하는 명령어
a.txt , b.txt 파일의 첫 10라인 출력하기
더보기
$ cat a.txt
hello 1
~~ 중략 ~~
hello 9
hello 10
hello 11
hello 12
hello 13
hello 14
$ cat b.txt
welcome 1
welcome 2
~~ 중략 ~~
welcome 10
welcome 11
welcome 12
welcome 13
welcome 14
$ head a.txt b.txt
==> a.txt <==
hello 1
hello 2
hi 3
hello 4
hello 5
hello 6
hello 7
hello 8
hello 9
hello 10
==> b.txt <==
welcome 1
welcome 2
hi 3
welcome 4
welcome 5
welcome 6
welcome 7
welcome 8
welcome 9
welcome 10
목차
| 옵션 | 의미 | 기타 |
| -c, --bytes=[-]NUM | NUM 바이트 출력 옵션 | - 사용시 끝부분에서 계산해 빼고 적용됨 |
| -n, --lines=[-]NUM | NUM 라인 출력옵션 | |
| -q, --quiet, --silent | 헤더 표시 제거옵션 | -q, -v 동시 적용시 뒤에옵션 적용됨 |
| -v, --verbose | 헤더 표시 옵션 | |
| -z, --zero-terminated | 구분자로 개행이 아닌 NUL 사용한 출력옵션 | |
| --help | 도움말 표시 | |
| --version | 버전표시 |
옵션
-c, --bytes=[-]NUM
: 파일/표준입력의 처음에서 NUM 바이트 까지 출력하는 옵션, 마이너스 입력시 마지막에서 바이트 계산후 출력
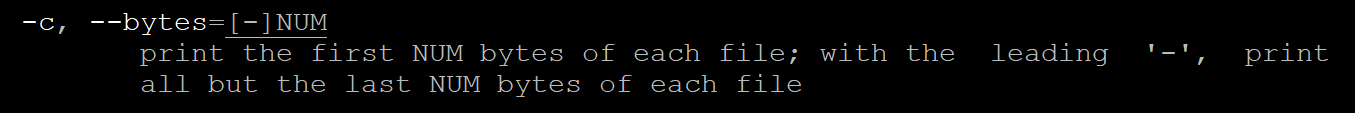
더보기
>> 처음부터 20 바이트 출력
$ head -c 20 a.txt b.txt
==> a.txt <==
hello 1
hello 2
hi
==> b.txt <==
welcome 1
welcome
>> -0 입력시 처음부터 끝까지 출력
$ head -c -0 a.txt b.txt
==> a.txt <==
hello 1
hello 2
hi 3
hello 4
hello 5
hello 6
hello 7
hello 8
hello 9
hello 10
hello 11
hello 12
hello 13
hello 14
==> b.txt <==
welcome 1
welcome 2
hi 3
welcome 4
welcome 5
welcome 6
welcome 7
welcome 8
welcome 9
welcome 10
welcome 11
welcome 12
welcome 13
welcome 14
>> 끝부터 50 바이트 제외하고 모두 출력하기
$ head -c -50 a.txt b.txt
==> a.txt <==
hello 1
hello 2
hi 3
hello 4
hello 5
hello 6
hello 7
hello 8
hello 9
==> b.txt <==
welcome 1
welcome 2
hi 3
welcome 4
welcome 5
welcome 6
welcome 7
welcome 8
welcome 9
welcome 1
>> 롱 옵션 사용하기
$ head --bytes -50 a.txt b.txt
$ head --bytes=-50 a.txt b.txt
==> a.txt <==
hello 1
hello 2
hi 3
hello 4
hello 5
hello 6
hello 7
hello 8
hello 9
==> b.txt <==
welcome 1
welcome 2
hi 3
welcome 4
welcome 5
welcome 6
welcome 7
welcome 8
welcome 9
-n, --lines=[-]NUM
: 처음부터 출력할 라인수 지정하기, 음수 입력시 끝에서 부터 NUM 라인 제거후 모두 출력함.

> " -n 10 "일 경우 "-10" 이라고 입력해도 동일하게 동작합니다.
더보기
$ head -n 10 a.txt
hello 1
hello 2
hi 3
hello 4
hello 5
hello 6
hello 7
hello 8
hello 9
hello 10
$ head -n 3 a.txt
hello 1
hello 2
hi 3
$ head --line 7 a.txt
hello 1
hello 2
hi 3
hello 4
hello 5
hello 6
hello 7
$ head --line=7 a.txt
hello 1
hello 2
hi 3
hello 4
hello 5
hello 6
hello 7
$ echo -e "hello\nHi" | head -n 2
hello
Hi
$ echo -e "hello\nHi" | head -n 1
hello
?>> 마이너스 입력시 끝에서 입력 라인만큼 빼고 출력합니다.
$ head --line=-5 a.txt
hello 1
hello 2
hi 3
hello 4
hello 5
hello 6
hello 7
hello 8
hello 9
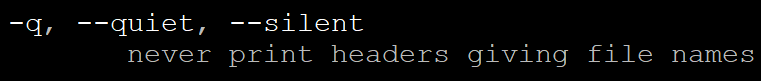
-q, --quiet, --silent
: 헤더 ( 파일이름)를 출력하지 않는 옵션
>> default
$ head -n3 a.txt b.txt
==> a.txt <==
hello 1
hello 2
hi 3
==> b.txt <==
welcome 1
welcome 2
hi 3
>> 파일이름 표시안하게 하기
$ head -q -n3 a.txt b.txt
hello 1
hello 2
hi 3
welcome 1
welcome 2
hi 3
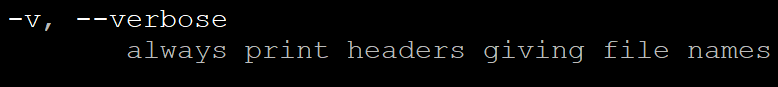
-v, --verbose
: 항상 헤더(파일이름) 표시옵션
> -q, -v 옵션 동시 사용하면 뒤에 나오는게 적용됩니다.
$ head -v -n3 a.txt
==> a.txt <==
hello 1
hello 2
hi 3
$ head -q -v -n3 a.txt
==> a.txt <==
hello 1
hello 2
hi 3
$ head -v -q -n3 a.txt
hello 1
hello 2
hi 3
-z, --zero-terminated
: 라인구분자가 개행이 아니고 NUL(0x00) 로 지정하는 옵션

$ cat a.txt
hello 1
hello 2hi 3hello 4
hello 5
hello 6
hello 7
hello 8
hello 9
hello 10
hello 11
hello 12hello 13
hello 14
$ hexdump a.txt
0000000 6568 6c6c 206f 3120 680a 6c65 6f6c 2020
0000010 0032 6968 2020 2020 3320 6800 6c65 6f6c <----- 0x10,0x1B번지 값 00
0000020 2020 0a34 6568 6c6c 206f 3520 680a 6c65
0000030 6f6c 2020 0a36 6568 6c6c 206f 3720 680a
0000040 6c65 6f6c 2020 0a38 6568 6c6c 206f 3920
0000050 680a 6c65 6f6c 2020 3031 680a 6c65 6f6c
0000060 2020 3131 680a 6c65 6f6c 2020 3231 6800 <---- 0x6f번지 값 00
0000070 6c65 6f6c 2020 3331 680a 6c65 6f6c 2020
0000080 3431 000a
0000083
>> null 로 끝나는 한줄 출력하기
$ head -z -n1 a.txt
hello 1
hello 2c
--help
: 도움말 출력
$ head --help
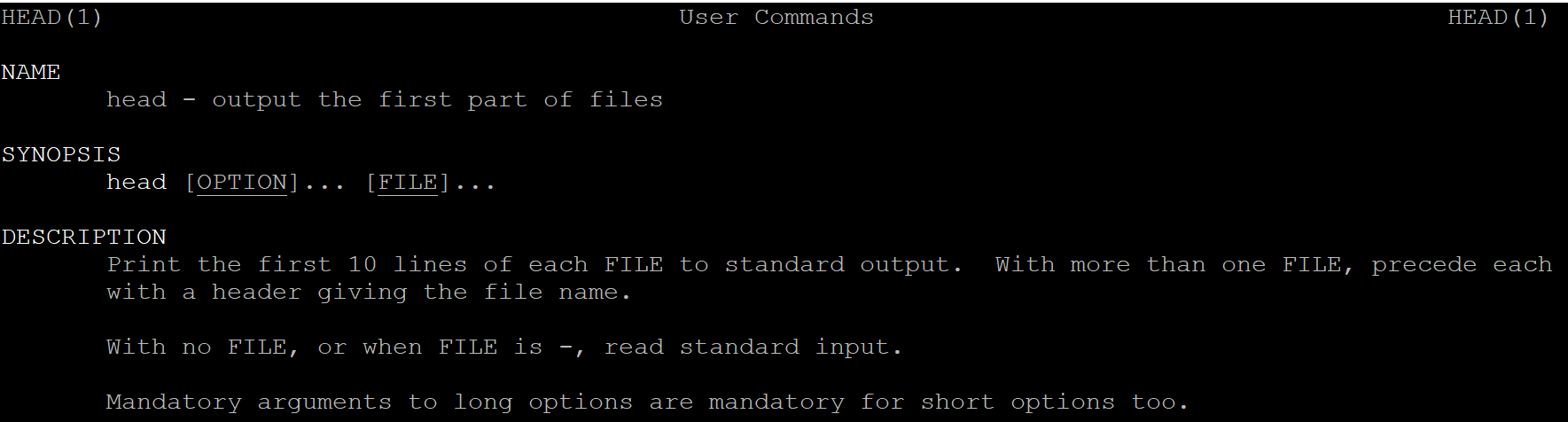
Usage: head [OPTION]... [FILE]...
Print the first 10 lines of each FILE to standard output.
With more than one FILE, precede each with a header giving the file name.
With no FILE, or when FILE is -, read standard input.
Mandatory arguments to long options are mandatory for short options too.
-c, --bytes=[-]NUM print the first NUM bytes of each file;
with the leading '-', print all but the last
NUM bytes of each file
-n, --lines=[-]NUM print the first NUM lines instead of the first 10;
with the leading '-', print all but the last
NUM lines of each file
-q, --quiet, --silent never print headers giving file names
-v, --verbose always print headers giving file names
-z, --zero-terminated line delimiter is NUL, not newline
--help display this help and exit
--version output version information and exit
NUM may have a multiplier suffix:
b 512, kB 1000, K 1024, MB 1000*1000, M 1024*1024,
GB 1000*1000*1000, G 1024*1024*1024, and so on for T, P, E, Z, Y.
Binary prefixes can be used, too: KiB=K, MiB=M, and so on.
GNU coreutils online help: <https://www.gnu.org/software/coreutils/>
Full documentation <https://www.gnu.org/software/coreutils/head>
or available locally via: info '(coreutils) head invocation'
--version
: 버전 출력
$ head --version
head (GNU coreutils) 8.32
Copyright (C) 2020 Free Software Foundation, Inc.
License GPLv3+: GNU GPL version 3 or later <https://gnu.org/licenses/gpl.html>.
This is free software: you are free to change and redistribute it.
There is NO WARRANTY, to the extent permitted by law.
Written by David MacKenzie and Jim Meyering.
반응형
