: 여러개의 파일들에 대한 이름 변경시 사용하는 명령어
Synopsis : rename [option] [perlexpr] [files]
files 에 선택된 파일의 이름을 perlexpr 에 맞게 변경합니다.
옵션은 있을수도 있고 없을경우도 있습니다.
매뉴얼 페이지
0> 도표
|
옵션
|
의미
|
기타
|
|
-v , --verbose
|
파일 이름 출력 옵션
|
목차 참조
|
|
-n, --no-act
|
실제 변경이 아닌 테스트 옵션
|
목차 참조 |
|
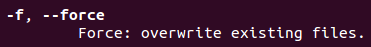
-f, --force
|
파일 존재시 overwrite 옵션
|
목차 참조 |
목차
옵션
-v 옵션
: 변경된 이름 출력 옵션

$ ls
a01.txt a02.txt b01.txt test01.txt test02.txt test03.txt
>> 확장자가 .txt 인 파일의 마지막에 .bak 추가하기
$ rename -v 's/\.txt$/\.txt\.bak/' *.txt
a01.txt renamed as a01.txt.bak
a02.txt renamed as a02.txt.bak
b01.txt renamed as b01.txt.bak
test01.txt renamed as test01.txt.bak
test02.txt renamed as test02.txt.bak
test03.txt renamed as test03.txt.bak
$ ls
a01.txt.bak b01.txt.bak test02.txt.bak
a02.txt.bak test01.txt.bak test03.txt.
-n 옵션
: 실제로 변경되는건 아니고 테스트 용 미리 적용한 내용 보여주는 옵션입니다.

$ ls
a01.txt.bak b01.txt.bak test02.txt.bak
a02.txt.bak test01.txt.bak test03.txt.bak
>> .txt.bak 파일 이름을 .txt으로 변경 테스트 (실제 적용은 안하고 테스트용)
$ rename -n 's/\.txt\.bak$/.txt/' *.txt.bak
a01.txt.bak renamed as a01.txt
a02.txt.bak renamed as a02.txt
b01.txt.bak renamed as b01.txt
test01.txt.bak renamed as test01.txt
test02.txt.bak renamed as test02.txt
test03.txt.bak renamed as test03.txt
>> 이름 변경 여부 체킹하기
$ ls
a01.txt.bak b01.txt.bak test02.txt.bak
a02.txt.bak test01.txt.bak test03.txt.bak
-f 옵션
: 파일 존재 시 강제 쓰기 옵션입니다.
$ ls
a01.txt a02.txt.bak test01.txt.bak test03.txt.bak
a01.txt.bak b01.txt.bak test02.txt.bak
>> a01.txt 파일이 존재할 경우 이름변경이 되지 않습니다.
$ rename 's/\.txt\.bak$/.txt/' *.txt.bak
a01.txt.bak not renamed: a01.txt already exists
>> -f 옵션 추가시 강제로 overwrite 적용해 줍니다.
$ rename -f 's/\.txt\.bak$/.txt/' *.txt.bak
$ ls
a01.txt a02.txt b01.txt test01.txt test02.txt test03.txt
< 기타>
에러 메시지
"Bareword "blabla" not allowed while "strict subs" in use at (eval 1) line 1. "
>> 문법에 맞지 않게 적었을 경우 나오는 메시지
$ rename a01.txt.bak a01.bak
Bareword "a01" not allowed while "strict subs" in use at (eval 1) line 1.
Bareword "txt" not allowed while "strict subs" in use at (eval 1) line 1.
Bareword "bak" not allowed while "strict subs" in use at (eval 1) line 1.
>> Synopsis : rename [option] [perlexpr] [files]
아래의 파일 이름에 들어가는 chromecast_nrf52_mouse_ 글자 제거하기
$ ls -1
chromecast_nrf52_mouse_disconnect_2nd.logcat
chromecast_nrf52_mouse_disconnect_3rd_del_timestamp.logcat
chromecast_nrf52_mouse_disconnect_3rd.logcat
chromecast_nrf52_mouse_disconnect_4th.logcat
chromecast_nrf52_mouse_disconnect_5th.logcat
chromecast_nrf52_mouse_disconnect_6th.logcat
chromecast_nrf52_mouse_disconnect_7th.logcat
chromecast_nrf52_mouse_disconnect_8th.logcat
chromecast_nrf52_mouse_disconnect_9th_del_timestamp.logcat
chromecast_nrf52_mouse_disconnect_9th.logcat
chromecast_nrf52_mouse_disconnect.logcat
chromecast_nrf52_mouse_pairing.logcat
chromecast_nrf52_mouse_reconnect_2nd.logcat
chromecast_nrf52_mouse_reconnect_3rd_del_timestamp.logcat
chromecast_nrf52_mouse_reconnect_3rd.logcat
chromecast_nrf52_mouse_reconnect_4th.logcat
chromecast_nrf52_mouse_reconnect_5th.logcat
chromecast_nrf52_mouse_reconnect_6th.logcat
chromecast_nrf52_mouse_reconnect_7th.logcat
chromecast_nrf52_mouse_reconnect_8th.logcat
chromecast_nrf52_mouse_reconnect_9th_disappear_del_timestamp.logcat
chromecast_nrf52_mouse_reconnect_9th_disappear.logcat
chromecast_nrf52_mouse_reconnect.logcat
$ rename 's/^chromecast_nrf52_mouse_//' chromecast*
$ ls
disconnect_2nd.logcat disconnect_6th.logcat disconnect.logcat reconnect_4th.logcat reconnect_9th_disappear_del_timestamp.logcat
disconnect_3rd_del_timestamp.logcat disconnect_7th.logcat pairing.logcat reconnect_5th.logcat reconnect_9th_disappear.logcat
disconnect_3rd.logcat disconnect_8th.logcat reconnect_2nd.logcat reconnect_6th.logcat reconnect.logcat
disconnect_4th.logcat disconnect_9th_del_timestamp.logcat reconnect_3rd_del_timestamp.logcat reconnect_7th.logcat
disconnect_5th.logcat disconnect_9th.logcat reconnect_3rd.logcat reconnect_8th.logcat
모든 소문자 이름을 대문자로 변경하기
$ ls
a01.txt a02.txt b01.txt test01.txt test02.txt test03.txt
$ rename 'y/a-z/A-Z/' *
$ ls
A01.TXT A02.TXT B01.TXT TEST01.TXT TEST02.TXT TEST03.TXT
: 위 구분에 사용된 y : (translation) 구문은
'y/charset1/charset2/'
앞뒤로 인덱스를 주어서 이름 변경하기
$ ls
123456789.tst abcdefghi.tst TEST03.TXT
>> 앞에서 4글자 뒤에서 5글자만 사용하기
$ rename -n 's/(?<=^.{4}).+(?=.{5}$)//' *.tst
123456789.tst renamed as 12349.tst
abcdefghi.tst renamed as abcdi.tst
: 위 구문에 사용된 s : substitution (대체)의 구문은
's/expr1/expr2/ [gi]'
>> expr1 표현을 expr2로 대체하라는 뜻입니다. g: global , i : case-insentive
rename 명령어 분석
>> rename 명령어 위치 찾기
$ which rename
/usr/bin/rename
>> 이파일은 심볼릭 링크 파일이라서 실제파일을 찾아야 합니다.
$ ls -al /usr/bin/rename
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 24 5월 25 2017 /usr/bin/rename -> /etc/alternatives/rename
$ ls -l /etc/alternatives/rename
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 16 5월 25 2017 /etc/alternatives/rename -> /usr/bin/prename
$ ls -al /usr/bin/prename
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 2987 11월 21 2018 /usr/bin/prename
/usr/bin/rename -> /etc/alternatives/rename -> /usr/bin/prename
>> 실제 파일이 prename 이네요. 무슨파일인지 file 명령을 실행 해 보면
$ file /usr/bin/prename
/usr/bin/prename: Perl script, ASCII text executable
>> perl script 라고 나오네요. 그럼 안의 내용을 head 이용해 5줄만 출력해 볼께요.
$ head -5 /usr/bin/prename
#!/usr/bin/perl -w
#
# This script was developed by Robin Barker (Robin.Barker@npl.co.uk),
# from Larry Wall's original script eg/rename from the perl source.
#
>> 첫줄에 perl 로 작성된 파일이라고 적혀 있네요.
==> /usr/bin/prename 소스 첨부합니다. ( 분석해 보실 분 참고하세요.)
#!/usr/bin/perl -w
#
# This script was developed by Robin Barker (Robin.Barker@npl.co.uk),
# from Larry Wall's original script eg/rename from the perl source.
#
# This script is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify it
# under the same terms as Perl itself.
#
# Larry(?)'s RCS header:
# RCSfile: rename,v Revision: 4.1 Date: 92/08/07 17:20:30
#
# $RCSfile: rename,v $$Revision: 1.5 $$Date: 1998/12/18 16:16:31 $
#
# $Log: rename,v $
# Revision 1.5 1998/12/18 16:16:31 rmb1
# moved to perl/source
# changed man documentation to POD
#
# Revision 1.4 1997/02/27 17:19:26 rmb1
# corrected usage string
#
# Revision 1.3 1997/02/27 16:39:07 rmb1
# added -v
#
# Revision 1.2 1997/02/27 16:15:40 rmb1
# *** empty log message ***
#
# Revision 1.1 1997/02/27 15:48:51 rmb1
# Initial revision
#
use strict;
use Getopt::Long;
Getopt::Long::Configure('bundling');
my ($verbose, $no_act, $force, $op);
die "Usage: rename [-v] [-n] [-f] perlexpr [filenames]\n"
unless GetOptions(
'v|verbose' => \$verbose,
'n|no-act' => \$no_act,
'f|force' => \$force,
) and $op = shift;
$verbose++ if $no_act;
if (!@ARGV) {
print "reading filenames from STDIN\n" if $verbose;
@ARGV = <STDIN>;
chop(@ARGV);
}
for (@ARGV) {
my $was = $_;
eval $op;
die $@ if $@;
next if $was eq $_; # ignore quietly
if (-e $_ and !$force)
{
warn "$was not renamed: $_ already exists\n";
}
elsif ($no_act or rename $was, $_)
{
print "$was renamed as $_\n" if $verbose;
}
else
{
warn "Can't rename $was $_: $!\n";
}
}
__END__
=head1 NAME
rename - renames multiple files
=head1 SYNOPSIS
B<rename> S<[ B<-v> ]> S<[ B<-n> ]> S<[ B<-f> ]> I<perlexpr> S<[ I<files> ]>
=head1 DESCRIPTION
C<rename>
renames the filenames supplied according to the rule specified as the
first argument.
The I<perlexpr>
argument is a Perl expression which is expected to modify the C<$_>
string in Perl for at least some of the filenames specified.
If a given filename is not modified by the expression, it will not be
renamed.
If no filenames are given on the command line, filenames will be read
via standard input.
For example, to rename all files matching C<*.bak> to strip the extension,
you might say
rename 's/\.bak$//' *.bak
To translate uppercase names to lower, you'd use
rename 'y/A-Z/a-z/' *
=head1 OPTIONS
=over 8
=item B<-v>, B<--verbose>
Verbose: print names of files successfully renamed.
=item B<-n>, B<--no-act>
No Action: show what files would have been renamed.
=item B<-f>, B<--force>
Force: overwrite existing files.
=back
=head1 ENVIRONMENT
No environment variables are used.
=head1 AUTHOR
Larry Wall
=head1 SEE ALSO
mv(1), perl(1)
=head1 DIAGNOSTICS
If you give an invalid Perl expression you'll get a syntax error.
=head1 BUGS
The original C<rename> did not check for the existence of target filenames,
so had to be used with care. I hope I've fixed that (Robin Barker).
=cut
~~~~ 계속 추가중
반응형
'리눅스 (linux) > 명령어' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 리눅스 grep 명령어 사용법 ( -r, -v, -E, -i, -s, -n, -h, -w, -f, -x) (0) | 2022.02.21 |
|---|---|
| 리눅스 history 명령어 사용법 (-c,-d,-a,-n,-r,-w,-p,-s) (0) | 2022.02.18 |
| 리눅스 find 명령어 사용법 (-P,-L,-H,-D,-type, -print0,-ls...) (0) | 2022.02.17 |
| 리눅스 echo 명령어 사용법 ( -n, -e , -E , --help) (0) | 2022.02.17 |
| 리눅스 mkdir 명령어 사용법 ( -m, -p, -v, -Z) (0) | 2022.02.16 |
